VIDAS® Acute Coronary Syndrome panel
Präzise Diagnostik bei Myokardinfarkt
VIDAS® HS Troponin I, VIDAS® CK-MB und VIDAS® Myoglobin* sind automatisierte, quantitative Tests zur Beurteilung von Myokardschädigungen.
- Hohe klinische Sensitivät und Spezifität für die Diagnostik bei akutem Myokardinfarkt und für die Risikostratifikation (Troponin I)
- 3 komplementäre Marker
- Zuverlässige Plattform für reaktionsschnelle Labore
Benötigen Sie weitere Informationen?
Das VIDAS® Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) Panel umfasst drei komplementäre Tests zur Beurteilung von Myokardschädigungen1, 2. In Verbindung mit einer klinischen Untersuchung und einem Elektrokardiogramm ermöglichen die Tests eine zeitnahe und präzise Evaluierung von Patienten mit Verdacht auf MI und unterstützen eine optimale Versorgung. Die Tests laufen auf den Geräten der VIDAS®-Familie und sind vor allem für die Notfalldiagnostik geeignet.
Komplementäre Marker unterstützen die Diagnostik bei akutem Myokardinfarkt (AMI)
Aufgrund der Spezifität für myokardiale Gewebeschädigungen ist kardiales Troponin I (cTnI) der bevorzugte Biomarker bei kardialer Nekrose2. Die schnelle Zunahme der cTnl-Konzentration (innerhalb von 3 bis 6 Stunden nach Einsetzen des Brustschmerzes) sowie die Tatsache, dass diese für 4 bis 7 Tage erhöht bleibt5, macht cTnI zum diagnostischen Marker bei Myokardinfarkt.
Die Messung der Proteinkonzentration des Isoenzyms MB der humanen Creatin-Kinase (CK-MB) wird für die Diagnostik des Myokardinfarkts empfohlen, wenn keine Tests für kardiales Troponin zur Verfügung stehen5. Die Konzentration der CK-MB steigt nach einem Infarkt ebenfalls sehr schnell an. Aufgrund der kürzeren Halbwertszeit kann dieses Enzym als Marker für einen Reinfarkt verwendet werden.
Myoglobin ist einer der ersten Biomarker bei Myokardschädigungen, der nach dem Auftreten eines Myokardinfarkts gemessen werden kann. Bei Patienten, die sich innerhalb von 6 Stunden nach Auftreten der Symptome vorstellen, kann die Testung von Myoglobin zusätzlich zum kardialen Troponin als Parameter für einen frühen Ausschluss eines ACS herangezogen werden5.
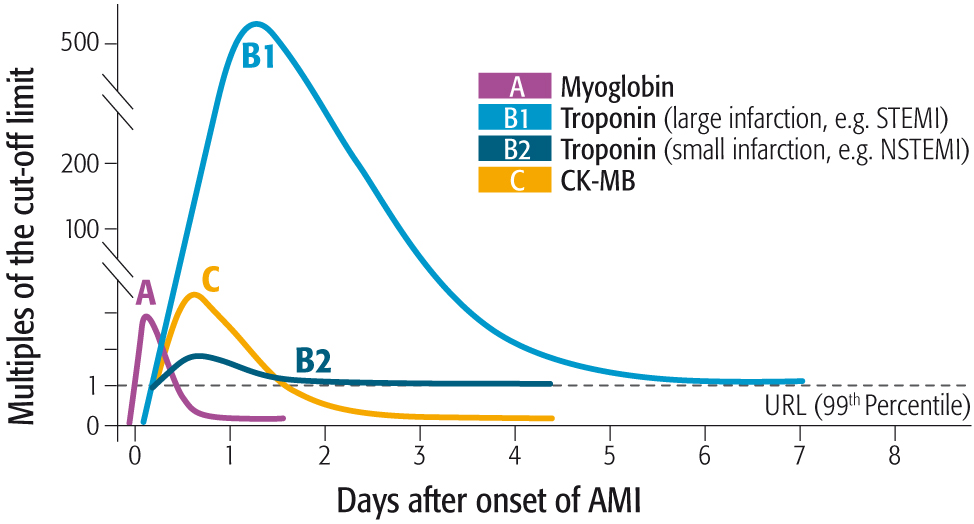
Temporäres Profil der Marker bei Myokardnekrose nach akutem Myokardinfarkt
(in Anlehnung an [6]).
Klinische Sensitivität und Spezifität von VIDAS® Troponin I Ultra
- Hohe klinische Sensitivität für die Diagnostik des Myokardinfarkts3 (siehe nachstehende Tabelle)
- Kurzfristige Risikostratifikation für eine schnelle Patiententriage und besseres Patientenmanagement3
- Sensitiver Test zur Identifizierung von Patienten mit ACS mit schlechten klinischen Ergebnissen4
Vorteile der VIDAS®-Lösung
- Zuverlässige und einfach zu bedienende Geräte mit direktem Zugriff und geringem Platzbedarf. Bestens angepasst an schnellreagierende Labore.
- Werkseitige Kalibrierung, Einzeltestformat reduzieren die Anzahl zusätzlicher Kontrollen**.
- Kurze Testdauer: VIDAS® HS Troponin I liefert Ergebnisse in nur 20 Minuten; vergleichbare Analysezeiten bieten VIDAS® CK-MB und Myoglobin.
- Reagenzien können sofort nach Entnahme aus dem Kühlschrank verwendet werden.
- VIDAS® NT-proBNP2 im umfangreichen VIDAS-Produktportfolio verfügbar.
* Bitte fragen Sie den für Sie zuständigen bioMérieux-Außendienstmitarbeiter nach der Produktverfügbarkeit in Ihrem Land.
** von lokalen Richtlinien abhängig.
Referenzen:
- Hamm CW, Bassand JP, Agewall S, et al. ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation. Eur Heart J 2011;32: 2999-3054.
- Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, et al., the Writing Group on behalf of the Joint ESC/ACCF/AHA/WHF Task Force for the Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction. Third universal definition of myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2012;33:2551-2567
- Apple FS, Smith SW, Pearce LA, et al. Use of the bioMérieux VIDAS® troponin I ultra assay for the diagnosis of myocardial infarction and detection of adverse events in patients presenting with symptoms of acute coronary syndrome. Clin Chem Acta 2008;390:72-75.
- Venge, P and Lindahl, B. Cardiac Troponin Assay Classification by Both Clinical and Analytical Performance Characteristics: A Study in Outcome Prediction. Clin Chem 2013;59:976-81.
- Morrow, DA, Cannon CP, Jesse JL, et al. National Academy of Clinical Biochemistry Laboratory Medicine Practice Guidelines: Clinical characteristics and utilization of biochemical markers in acute coronary syndromes. Circulation. 2007; 115: 356-75.
- Wu AH, Apple FS, Gibler WB et al. National Academy of Clinical Biochemistry Standards of Laboratory Practice: recommendations for the use of cardiac markers in coronary artery diseases. Clin. Chem. 1999; 45: 1104-1121.
- Package insert, VIDAS Troponin I Ultra (TNIU), CE-mark. August 2010.
| VIDAS® CK-MB | VIDAS® Myoglobin | |
|---|---|---|
| Bestellnummer | 30421 | 30446 |
| Tests/Packung | 30 | 30 |
| Probenmaterial | Serum, Plasma (Heparin, EDTA) | Serum, Plasma (Heparin) |
| Probenmenge | 250 µl | 150 µl |
| Kalibrierstabilität | 14 Tage | 14 Tage |
| Analysedauer | 30 Minuten | 17 Minuten |
Weitere technische Angaben finden Sie auf www.myvidas.com.
Bitte fragen Sie den für Sie zuständigen bioMérieux-Außendienstmitarbeiter nach der Produktverfügbarkeit in Ihrem Land.
WEITERFÜHRENDE LITERATUR
Troponin I
- Apple FS, Smith SW, Pearce LA, et al. Use of the bioMérieux VIDAS® troponin I ultra assay for the diagnosis of myocardial infarction and detection of adverse events in patients presenting with symptoms of acute coronary syndrome. Clin Chem Acta 2008;390:72-75.
- Venge, P and Lindahl, B. Cardiac Troponin Assay Classification by Both Clinical and Analytical Performance Characteristics: A Study in Outcome Prediction. Clin Chem 2013;59:976-81.
CK-MB
Myoglobin
RICHTLINIEN
- Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, et al., the Writing Group on behalf of the Joint ESC/ACCF/AHA/WHF Task Force for the Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction. Third universal definition of myocardial infraction.Eur Heart J.2012;33:2551-2567.
- Hamm CW, Bassand JP, Agewall S, et al. ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation. Eur Heart J 2011;32: 2999-3054.
- Thygesen K, Mair J, Katus H, et al. Study Group on Biomarkers in Cardiology of the ESC Working Group on Acute Cardiac Care. Recommendations for the use of cardiac troponin measurement in acute cardiac care. Eur Heart J. 2010;31:2197-204.
- Jneid H, Anderson JL, Wright RS, et al. 2012 ACCF/AHA focused update of the guideline for the management of patients with unstable angina/non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60:645-681
- Morrow DA, Cannon, CP, Jesse, RL, et al. National Academy of Clinical Biochemistry Laboratory Medicine Practice Guidelines: Clinical characteristics and utilization of biochemical markers in acute coronary syndromes. Circulation. 2007; 115: e356-75.
NÜTZLICHE LINKS
- European Society of Cardiology: http://www.escardio.org/Pages/index.aspx
- American College of Cardiology: http://www.cardiosource.org/acc
- National Academy of Clinical Biochemistry (NACB): http://www.aacc.org/members/nacb/Pages/default.aspx#
Weitere wissenschaftliche Quellen und Informationsmaterial finden Sie auf www.myvidas.com







